Title
Which type of EV is right for you
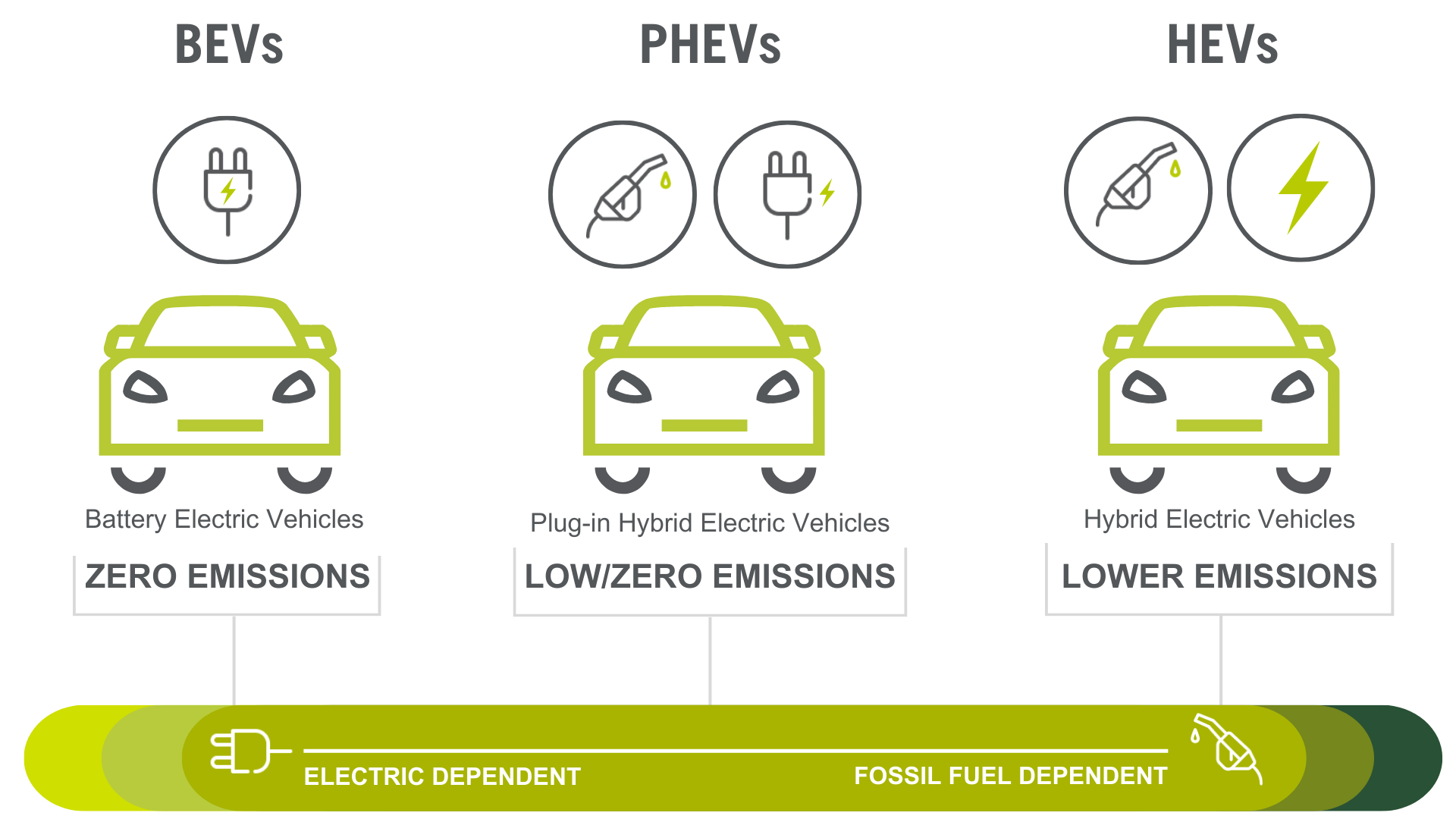
There are three main types of Electric Vehicles (EVs): Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs), which run solely on electricity; Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs), which can operate on both electricity and gasoline; and Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs), which do not plug into the grid but have batteries to help reduce fossil fuel consumption.
In addition to these three EV types, there are also Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs). These vehicles use a clean and innovative technology where electricity is generated onboard through a reaction between hydrogen and oxygen.
You can use the following tools to help find the right EV to suit your budget and driving needs.
Considering a switch to electric? Use the EV Calculator to explore potential cost savings and compare models based on your driving habits.
Title
Related Content
Have questions? Email us at EV@alectrautilities.com
